高负值度数镜片设计
作者:GREGORY L. STEPHENS and JOHN K. DAVIS
译者: Lisa Huang
原文出处:http://www.eyecalcs.com/DWAN/pages/v1/v1c051b.html#ato
负值度数特别高的处方(大于约10.00D)镜片边缘很厚,影响美观,且在某些镜架上很难安装。这个问题可以通过尽可能为患者提供可行的小镜架来缓解,同时,高指数塑料也可以帮上忙。虽然会有离轴横向色差,大部分患者还是可以忍受这种色差的,因为镜片更厚更轻了。高负值度数镜片一般两面都是凹的,因为光学实验室很难把度数全部铣磨在镜片的一个面上。轻薄的上色和防反射镀膜可以减弱镜片边缘附近的多环反射(近视环)。
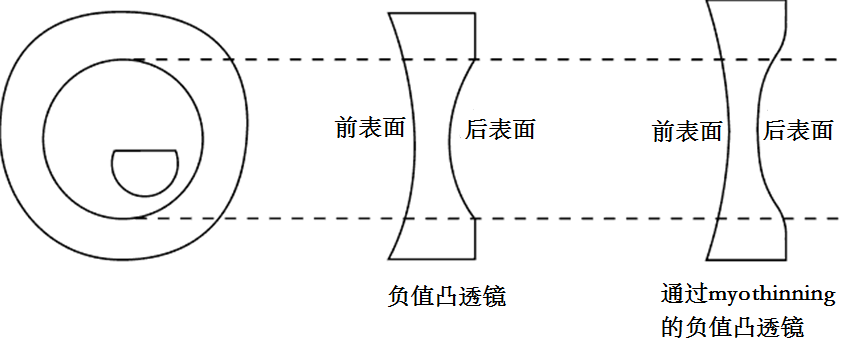
高负值度数镜片偶尔会用凸镜的形式制作(图17)。从本质上来说,它是在镜片后表面切割掉较厚的边缘,使外缘载体不再有光学作用,同时直径40mm的中心碗状部分可以做到折射矫正。当镜片的前表面较平时,载体的后表面也会平,这样的镜片被称为myodisk。载体的连接处和负值凸透镜镜片的碗状部分可以混合在一起,从而使它不那么明显,也没有了锋利的边缘。这个过程通常被称为myothinning(见图17)。由于它们脆弱的外形,所有高负值度数镜片必须小心使用。
|
图17为负值凸透镜和通过myothinning的负值凸透镜的正视图和横截面图。 |
参考文献
1. Schwartz JT, Ogle KN: The depth of focus of the eye. Arch Ophthalmol 61:578, 1959
2. Campbell FW: The depth of field of the human eye. Optica Acta 4:157, 1957
3. Peters HB: The relationship between refractive error and visual acuity at three age levels. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom 38:194, 1961
4. Sloan LL: Measurement of visual acuity: A critical review. Arch Ophthalmol 45:704, 1951
5. Allen MJ: Vision and Highway Safety, p 56. Philadelphia: Chilton, 1970
6. Davis JK: Prescribing for visibility. Probl Optom 2:131, 1990
7. Richards OW: Vision at levels of night road illumination: XII. Change of acuity and contrast sensitivity with age. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom 43:313, 1966
8. Pitts DG: The effects of aging on selected visual functions: Dark adaptation, visual acuity, stereopsis, and brightness contrast. In Sekuler R, Kline D, Dismukes K (eds): Aging and Human Visual Function, pp 131–159. New York: Alan R Liss, 1982
9. American National Standard for Ophthalmics-Prescription Ophthalmic Lenses-Recommendations. ANSI Z80.1-1995. New York: American National Standards Institute, 1995
10. Owens DA: The resting state of the eyes. Am Scientist 72:378, 1984
11. Tunnacliffe AH, Hirst JG: Optics, pp 178–213. 2nd ed. London: Association of British Dispensing Opticians, 1996
12. Fannin TE, Grosvenor T: Clinical Optics, pp 134–141. 2nd ed. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1996
13. Atchison DA: The clinical importance of spectacle lens base curves. Clin Exp Optom 69:31, 1986
14. Davis JK: Geometric optics in ophthalmic lens design. Proc Soc Photo-Optical Instrum Engineers 39:65, 1973
15. Prentice CF: A metric system for numbering and measuring prisms. Arch Ophthalmol 19:64–75, 128–135, 1890
16. Bechtold EW, Langsen AL: The effect of pantoscopic tilt on ophthalmic lens performance. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom 42:515, 1965
17. Atchison DA, Tame SA: Sensitivity of off-axis performance of aspheric spectacle lenses to tilt and decentration. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 13:415, 1993
18. Davis JK: A polycarbonate ophthalmic prescription lens series. Am J Optom Physiol Opt 55:543, 1978
19. Smith WJ: Modern Optical Engineering: The Design of Optical Systems, pp 281–325. 2nd ed. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 1990
20. Atchison DA: Spectacle lens design—development and present state. Aust J Optom 67:97, 1984
21. Davis JK, Fernald HG, Rayner AW: The design of a general purpose single vision lens series. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom 42:203, 1965
22. Davis JK, Fernald HG, Rayner AW: An analysis of ophthalmic lens design. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom 41:400, 1964
23. Davis JK, Fernald HG, Rayner AW: The Tillyer Masterpiece Lens: A Technical Discussion. Southbridge, MA: American Optical, 1964
24. Davis JK, Fernald HG, Rayner AW: Ophthalmic lens series. US Patent 3,434,781, 1969
25. Ogle KN: Researches in Binocular Vision, p 125. New York: Hafner, 1972
26. Rabbetts RB: Bennett and Rabbetts' Clinical Visual Optics, p 236. 3rd ed. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1998
27. Linksz A, Bannon RE: Aniseikonia and refractive problems. Int Ophthalmol Clin 5:515, 1965
28. Enoch JM: Management of aniseikonia after intraocular lens implantation or refractive surgery. J Refract Surg 13:79, 1997
29. Polasky M: Aniseikonia Cookbook II. Columbus: Ohio State University College of Optometry, 1990
30. Stephens GL, Polasky M. New options for aniseikonia correction: The use of high index materials. Optom Vis Sci 68:899, 1991